



Alternative Programmes in Poultry Farming Proposed by Filavie
Alternative programmes in poultry farming have been proposed by Filavie in the continuity of the French plan, Ecoantibio 2012-2017, aimed at reducing antibiotic resistance. The French plan Ecoantibio 2012-2017 is before any, an awareness of the rise of the antibiotic resistance of bacteria both in human and veterinary medicine. In 2009, European Commission estimated that 25,000 deaths in Europe were due to bacteria resistant to antimicrobial treatments. In breeding activity, the deficit of performance would amount to €1.5 billion every year. Since 2006, it has been forbidden in France to use antibiotic additives as growth promoters in animal feed. The use of antibiotics is nowadays reserved for the therapeutic interventions under veterinary prescription.
The French plan Ecoantibio 2012-2017 is before any, an awareness of the rise of the antibiotic resistance of bacteria both in human and veterinary medicine. In 2009, European Commission estimated that 25,000 deaths in Europe were due to bacteria resistant to antimicrobial treatments. In breeding activity, the deficit of performance would amount to €1.5 billion every year. Since 2006, it has been forbidden in France to use antibiotic additives as growth promoters in animal feed. The use of antibiotics is nowadays reserved for the therapeutic interventions under veterinary prescription.
Antibiotic resistance appears under several aspects:
- The capacity of bacteria to adapt itself and to survive after an antibiotic treatment
- An over-consumption of antibiotics for therapeutic purposes but used in preventive as well in curative programmes. As far as prevention is concerned, we are not sure to target a precise bacterial threat
- A "wear" of the present molecules on the market, with not only very few introductions of new antibiotics these last 15 years but also reduced perspectives of appearance of new molecules. Furthermore, it is the human medicine which will take advantage of this progress and not the veterinary therapeutic arsenal.
Through a more rational use of antibiotics in livestock, Ecoantibio plan foresees a reduction in their consumption by 25 per cent by 2017.
This plan is divided into five areas and 40 measures, of which nine are to develop alternatives to avoid the use of antibiotics (Area 2). These measures concern the sanitary prophylaxis, and the medical prophylaxis is to say the use of autogenous vaccines to combat specific bacterial diseases. In measure 19, the evaluation of alternative methods or programmes is formalised.
Barrier Floras
A preferred route against bacterial diseases outside antibiotics is the area of barrier flora or competition flora. The principle is to oppose to pathogenic bacteria, "good" bacteria or commensal bacteria, naturally present in the environment and in the organism of animals, particularly in the intestinal tract. Their role is essential in digestion, regulation and assimilation of nutrients in monogastric animals: poultry, pigs and calves.
This is an aerobic flora consisting of Lactobacillus, Bacillus and Pediococcus. The mode of action is simple: being intensively and regularly distributed, competition flora will colonise its environment and prevents the growth of pathogenic bacteria. Its action is more effective when the settlement is preventive: priority to the first occupant.
Criteria for Choosing a Good Barrier Flora
Since the 1980s, the mode of action of flora is well known and has given birth to probiotics with mixed reviews about their effectiveness. A new generation of flora took over since about 2005 with a more rational approach and a more controlled mode of production.
The most appropriate cocktail
Several objectives must be met to obtain the best possible efficiency of a barrier flora:
- Extend the range of activity for a maximum power against the major bacterial diseases
- Provide a sufficiently concentrated product to deeply colonise the surroundings (environment, digestive tract), with the suitable application programme
- A broad spectrum of activity does not conflict with a more specific action against bacteria such as salmonella. For this purpose, the introduction of lactobacillus is required.
- Each strain of bacteria should be well represented in the cocktail, not being "stifled" by the other strains. The production process must meet a consistent quality, from one batch to the other.
|
Lactobacillus, a so fragile small pet In all Filaflor range products, we find eight strains of Bacillus, they are sporulating aerobic bacteria. Spores are bacterial forms of resistance (like bacterial seed!). In contact with a favourable environment, they will 'germinate' and create new generations of bacteria. The enzymatic production allows to digest organic material. Filaflor Compost consists of these eight strains of bacteria, spores remain active at room temperature, resulting in product shelf life of 24 months. When it comes to distributing flora in drinking water, the provision of 'lactobacillus' (Lactococcus and Pediococcus) is fundamental; in fact, these bacteria will live in symbiosis with Bacillus and most of all will strongly acidify the intestinal environment, yet few pathogenic bacteria are resistant to acidification. Lactobacillus is then a major player in the anti-Salmonella and anti-E. coli fight. But their presence at high concentration in barrier flora is difficult: they do not sporulate and vegetative forms are fragile or even very fragile. Heating and/or drying process will decrease their title irreparably, so we cannot maintain high concentration in powder form. This explains why the first batches of Filactis were only under frozen presentation. Then Filavie researchers were able to keep the Lactobacillus in liquid form, but with a six-month shelf life. In July 2013, a new organic stabiliser has maintained a high titre for 12 months: this is the latest formulation of Liquid Filactis. |
Once these objectives are well integrated into the specifications of the product, the implementation of the manufacturing becomes very clear.
The Filavie option
Filavie is a manufacturer of commercial vaccines and bacterial autogenous vaccines; technology is well mastered for cultivating any kind of bacteria. The answers to the specifications above came naturally.
- Provide a broad spectrum of activity: Filavie for its flagship product, Liquid Filactis, selected 12 strains of bacteria deposited at the Institut Pasteur, from the genera Lactobacillus, Bacillus and Pediococcus
- The multiplication techniques help to ensure a shelf life of 12 months
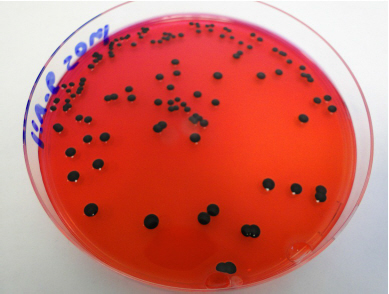
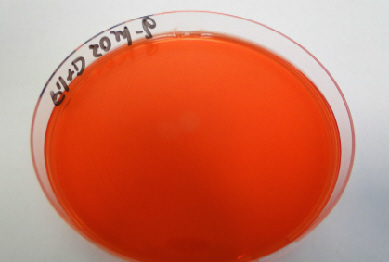
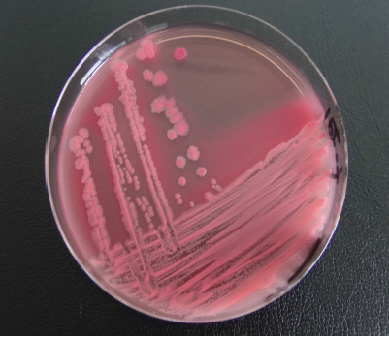
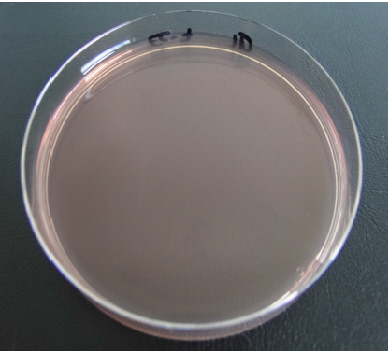
- Laboratory tests showed a competitive activity specific anti-Salmonella and anti-E. coli (see photos below of bacterial colonies, with or without barrier flora). Lactobacillus plays a major role on the one hand in acidification of the environment, and on the other hand, in secretion of probiotics.
- The criterion of representativeness of each strain of bacteria is provided by the mode of production. A flora product can be produced by fermentation of a multi strains inoculum, but the multiplication of bacteria is more or less anarchic and it results in a product of undefined composition and varies from one batch to another. The other system adopted by Filavie is to multiply each strain independently and make the mixture only after obtaining proper title of each bacterial strain. This technique is a guarantee of quality of the final product for each production lot.
Field and Programmes of Application
There are currently four areas of application barrier floras: "biological disinfection" on surfaces and equipment, colonisation of the gut by drinking water or reconstituted milk, nebulisation in the hatchery and composting by CMO (Complex of Micro-Organisms).
| User testimonials: a guaranteed profitability and a healthy organic livestock production
One million broiler French integration: 22 buildings tested compared to 28 control buildings. The 'friendly' bacteria of Filactis added to drinking water, colonise the digestive tract of animals and are found naturally in the litter. Aerobic fermentation acts by drying litter and reduces ammonia odours. A better litter has important consequences for the comfort and health of animals. Pododermatitis greatly dropped. A decrease of 47 per cent of breast lesions on the female (which are kept longer) and 22 per cent on males has been recorded. Sowed litter will continue its evolution into compost as soon as the swaths are built after the departure of the animals. Female ducks farm of Jean-Claude Bourget in La Chapelle-St-Florent, France: For this farm of near 20,000 subjects, the change is uplifting and definitive. The farmer applies Filactis Liquid in drinking water during rearing and Filaflor Compost just before the swath formation. The litter is eliminated once a year. In addition to an enhanced health status thanks to the Filactis competition flora against undesired bacterial contaminants, no antibiotic is administered to animals and compost is valued at €30 per ton ex-farm. The investment amounts to renting a manure spreader to form the swaths and the cost of products. Watch out, Filavie flora only works with a substrate with 40 per cent dry matter; we must provide sufficient organic material (in this case chopped straw) to obtain a good result, but it was already a necessity even before the use of flora. |
- The 'biological disinfection':The term is not really appropriate since no standard disinfectant is used to kill unwanted bacteria, but good bacteria are implanted in the environment to block the bad bacteria: this is the concept of biological control by competition. We apply a solution of Filafilm Liquid by spray on the immediate environment of the animals, floor, walls, ceiling and equipment. When a conventional disinfectant will not be able to penetrate porous materials, bacteria, however, will find multiplication niches which prevent unwanted bacteria implantation. Program: one application before start of rearing, repeat once or twice, depending on the duration of the production cycle in the presence of animals, since there is no toxicity of the product.
- Colonisation of the digestive tract: The Filactis Liquid, cocktail of 12 aerobic bacteria, including four strains of lactobacillus, is diluted in drinking water for poultry from day old at a rate of 100ml (to be diluted), for 10 to 20,000 subjects according to the type of livestock. For calves and pigs, it takes 100ml of Filactis Liquid for 15 tons live weight. Programmes vary from once per day in severe threat of contamination by pathogenic bacteria to once per week for prevention in case of minor risk of contamination.
- In the hatchery: Eggs can be nebulised at farm level or in the hatchery, at the transfer from incubators to hatchers at a rate of 2ml of Filactis Liquid diluted for 500 eggs. Day-old chicks may also be nebulised at the dose of 5ml of Filactis Liquid diluted in 20 ml of water, for 100 chicks.
- Composting: The Filaflor Compost is a cocktail of eight strains of Bacillus spore-forming bacteria. Thanks to it, you can make your own compost on the farm from different manures upon an average humidity of 60 per cent. In 42 days, you will obtain a 'sanitised' product that is to say with very low levels of undesirable bacteria. This is achieved thanks to a rise in temperature to 65 to 70°C for several days or weeks, due to aerobic fermentation maintained by the good bacteria. The Filaflor Compost is applied to the litter before windrowing or directly on the windrows. The dosage is 1 litre per 10 tons of manure. The infrastructure consists of a concrete or at least stabilised area, with a protection against bad weather and keeping aeration of the windrows. There is no need of turning windrows nor of forced ventilation. The method thus has a very favourable carbon footprint. The same result is obtained if the manure comes from litter of animals treated with the Filactis Liquid in the drinking water, since the flora is rejected in the feces and therefore in the litter to be composted.
Results and Advantages
The implementation of the above programmes has achieved positive results:
- The fight against salmonella and other enteric bacteria such as E. coli and Clostridia. Some farms, positive in Salmonella before treatment became negative.
- The farms treated with barrier floras no longer use antibiotics; doing so, we are fully entering into the philosophy of the plan Ecoantibio 2012-2017, under the heading of alternative programmes to antibiotic use.
- Most often, real production bonuses are recorded by improving nutrient absorption, better litter (lower leg problems and breast blisters on broilers), and a more pleasant environment since the aerobic fermentation produces very little noxious gas like ammonia.
- Composting becomes simple, time and money saving as well as environmentally friendly.
Conclusions
The use of barrier flora is one amongst available means to solve the problem of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria, but it deserves undoubtedly a wider application provided of course to use appropriate products and methods.
Recall that floras Filavie have been validated by the Food and Environment Regional Office in Brittany as accredited method for farm composting.
Finally, all Filavie’s floras got the 'organic label', allowing any farmer under this label to very easily justify the use of Filaflor range vis-à-vis the Official Organic Quality Controller.
December 2013








