FDA Publishes Report on Antibiotic Use
US - The FDA has published its '2009 Summary Report on Antimicrobials Sold or Distributed for Use in Food-Producing Animals'.Section 105 of the Animal Drug User Fee Amendments of 2008 (ADUFA) (110 P.L. 316; 122 Stat. 3509) amended section 512 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the act) (21 U.S.C. 360b) to require that sponsors of applications for new animal drugs containing an antimicrobial active ingredient submit an annual report to the Food and Drug Administration on the amount of each such ingredient in the drug that is sold or distributed for use in food-producing animals, including information on any distributor-labeled product. This legislation was enacted to assist FDA in its continuing analysis of the interactions (including drug resistance), efficacy and safety of antibiotics approved for use in both humans and food-producing animals (H. Rpt. 110-804).
Each report submitted to the FDA must specify:
- the amount of each antimicrobial active ingredient by container size, strength, and dosage form
- quantities distributed domestically and quantities exported, and
- a listing of the target animals, indications and production classes that are specified on the approved label of the product.
Sponsors of antimicrobial drug products that are approved and labeled for more than one food-producing animal species are not required to report sales and distribution information for each individual animal species. Only total product sales information is required. The first report must be submitted not later than 31 March 2010, and each year's report will provide monthly sales and distribution data for the preceding calendar year. These reports are separate from periodic drug experience reports that are required under 21 CFR 514.80(b)(4).
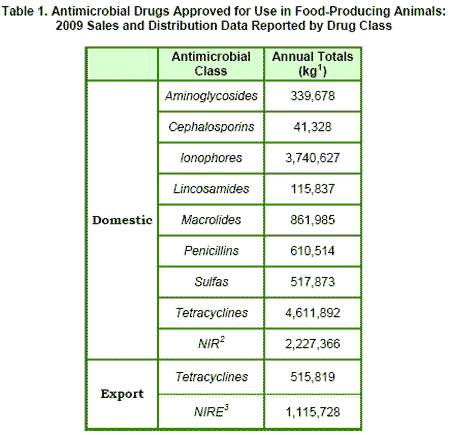
Section 105 of ADUFA also directs the FDA to make annual summaries of the reported information publicly available. In accordance with statutory requirements designed to protect confidential business information, annual sales and distribution data will be summarized by drug class and only those antimicrobial classes with three or more distinct sponsors of approved and actively marketed animal drug products are independently reported. Antimicrobial classes with fewer than three distinct sponsors are reported collectively as 'Not Independently Reported' (NIR) if the product was marketed domestically or 'Not Independently Reported Export' (NIRE) if the product was exported.
The number of distinct sponsors in a particular antimicrobial class is determined by two criteria:
- the sponsor must be named in 21 CFR 510.600 as the holder of an approved application for an animal drug product in that particular class on the last day of the annual reporting period, and
- the sponsor must have actively sold or distributed such animal drug product at some point during that annual reporting period.
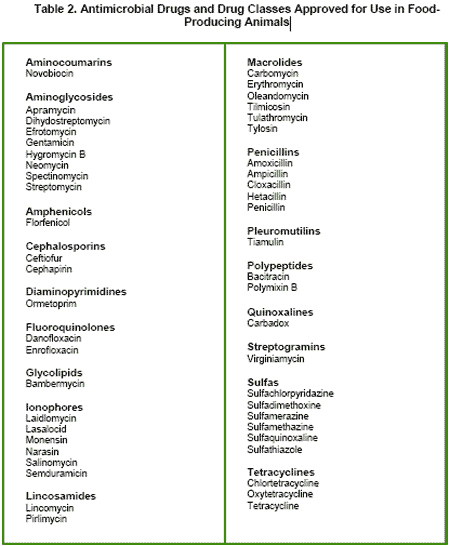
FDA's annual summary report for 2009 is presented in Table 1. The annual totals provided in Table 1 reflect all approved uses of all dosage forms (e.g. injectable, oral, medicated feed) of the identified classes of actively marketed drugs in food-producing animals. Table 2 lists the 17 antimicrobial drug classes represented in the report. As reference, this table also lists the specific drugs in each class for which there are approved animal drug products. However, the fact that an animal drug product is approved does not necessarily mean that it was actively marketed during this particular annual reporting period.
This summary report includes antimicrobial drugs that are specifically approved for antibacterial uses or are known to have antibacterial properties. Anti-fungal and anti-viral drugs are not included in this report because, with the exception of formalin and hydrogen peroxide water immersion products, there are currently no approved drug products actively marketed for these purposes in food-producing animals.