Food and Feed Safety in the EU
An overview of the current and possible future regulations covering food and feed safety in the European Union, as reported by avec, the Association of Poultry Processors and Poultry Trade in the EU Countries, in its annual report for 2011.
The EU poultry industry cares for the health of consumers as well as that of its poultry. Salmonella levels are decreasing and our industry is committed to fight the challenges of Campylobacter and to find the best solutions for using reformatory medicines in a prudent and responsible way.
Salmonella Criteria for Poultry Meat
The proposal of the Commission has been adopted by the SCoFCAH and is expected to come into force this month, December 2011. From then, Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium must be absent in sample of 25g.
Poultry meat Salmonella serotyping at farm level is required and introduced for the handling of those flocks in the slaughterhouse. The food business operator is responsible for the risk assessment and risk management but with regard to the control of Salmonella, an agreement with the supervising competent authority is crucial.
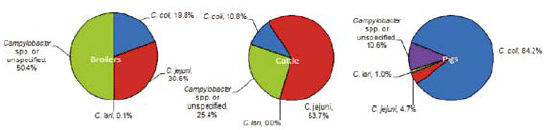
[Pic source: EFSA, 2011]
EFSA and ECDC Zoonoses Report
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) have published their annual report on zoonosis and food-borne outbreaks in the EU for 2009. The report shows Salmonella cases in humans fell by 17 per cent in 2009, marking a decrease for the fifth consecutive year. The report also shows that between 2008 and 2009, the number of laying flocks infected with Salmonella fell by nine per cent.
Campylobacteriosis remained the most reported zoonotic disease in humans, showing a slight increase with 198,252 cases in 2009 compared to 190,566 in 2008 (+4 per cent). In foods, Campylobacter, which can cause diarrhoea and fever, was mostly found in raw poultry meat and in live animals.
EFSA's Advice on Reduction of Campylobacter in Chickens
In the report published in April 2011, EFSA evaluates the risks of Campylobacter and suggests measures to be taken at farm and slaughterhouse level and during transport. EFSA's suggestions for interventions like irradiation, freezing and chemical treatment of the meat are not realistic options since they do not comply with consumer demands for fresh poultry meat. avec disagrees with the use of chemical substances in the process but could embrace use of an organic substance if the consumers agree to this.
avec can advocate a reduction of Campylobacter but not a zero tolerance, which may only be possible to obtain using methods like irradiation.
| To ensure the safety of food, consumers also have an important role to play. The core messages in the 'Five Keys To Safer Food Manual' of the World Health Organization's (WHO) are (1) keep clean; (2) separate raw and cooked; (3) cook thoroughly; (4) keep food at safe temperatures; and (5) use safe water and raw materials |
AMR – Antimicrobial Resistance
In March 2011, avec delivered input to the consultation of European Medicine Agency (EMA) on antimicrobial resistance. In April 2011, the Parliament called for tougher controls on the use of antibiotics in animal production. avec is committed to a responsible use of antimicrobials in the animal production and asks for a harmonisation of the EU monitoring of the use. The possible conflicts between the prescription and administration of medicines should be clarified. Once initiatives become legislation, third countries exporting to the EU must comply with the same measures.
In November 2009, the US and the EU established a transatlantic task-force on AMR. EPB and avec replied in December 2010 to a consultation on the content of the task-force to the Commission. The results and suggestions of TATFAR for future cooperation will be presented in an US-EU summit in fall 2011. The political leaders shall decide if the cooperation continues.
Antimicrobial Treatment (AMT) or Pathogen-Reducing Treatment (PRT)
Two dossiers have been submitted to BIOHAZ/EFSA for substance evaluation. One dossier concerns beef carcass and one covers poultry carcass decontamination.
avec closely follows the WTO-notified dispute between the US and the EU on the EU restriction to imports of US poultry meat treated with pathogen reducing chemicals – mainly chlorine based. No new developments have taken place this year and the arbiters in the panel have not been nominated yet.
Revision of the Hygiene Package
The ‘Hygiene” Regulations 852/2004 – 853/2004 – 854/2004 hygiene and controls of food of animal origin in force since 2006 lay down rules for the food chain ‘from stable to table’, that is food safety throughout the food chain starting with primary production. Currently, the issues under revision concerning avec deal with the definition of mechanically separated meat (MSM), meat preparations and meat products and ‘fresh’ and ‘frozen&sdquo;.
avec organised a workshop in 2011 on food safety issues and has given its comments to the Commission on the issues mentioned. An impact assessment of possible amendments is on-going.
Mechanically Separated Meat (MSM)
avec has followed the Histalim project to develop a methodology to assess the meat destruction index of MSM. The methodology has been assessed and approved by Association Française de Normalisation (AFNOR) and European Committee for Standardization (CEN). avec is strongly urging the Commission to agree to an objective and acceptable tool to differentiate between the different types of meat obtained and that the technological progress in the industry is acknowledged.
Modernisation of Meat Inspection
Based on the experience of applying the Hygiene Regulations 852/853 and 854/2004, the Commission aims to modernise the meat inspection in EU slaughterhouses by developing a risk-based approach for considering specific hazards or production systems. Food safety is not ensured by visual inspection of the poultry meat alone. Risk assessment and management must be supplemented by microbiological testing of the meat.
avec is of the opinion that meat inspection should act to minimise the actual risk, not continue to pursue outdated requirements. The Food Business Operator (FBO) has the responsibility and should demonstrate that he is controlling efficiently the food safety and is respecting the rules with regard to animal health and welfare.
Categorisation of Hatchery By-Products
Following Regulation 1069/2009 laying down health rules as regards animal by-products and derived products not intended for human consumption some of the hatchery by-products moved from category 3 into category 2 including ‘dead in shell poultry’.
The Commission has requested EFSA for an opinion about a Dutch study which concluded based upon a risk assessment that these by-products could be classified under category 3. A critical scientific opinion of EFSA was published in July 2011.
Reintroduction of Processed Animal Protein (PAP)
The Commission has presented a communication (SANCO/10843/2011) outlining the reintroduction of the use of PAP and amending Regulation 999/2001 laying down rules for the prevention, control and eradication of certain transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Dedicated processes respecting the intra-species recycling are available and avec is pleased that the Parliament has endorsed the proposal of the Commission. The proposal confirms the safety, feed value and environmental importance of processed animal protein (PAP).
avec hopes that the proposal can enter into force in 2012. The ban on feeding animal proteins to ruminants remains in place, as does the ban on intra-species recycling.
Community Guide: "Principles to Manage Salmonella Control in Feed"
According to Article 5(3) of Regulation 183/2005, feed business operators shall comply with specific microbiological criteria and take measures or adopt procedures necessary to meet specific targets with the view to minimise Salmonella in feed. All Salmonella serotypes in feed are targeted and all operators in the feed (supply) chain are included.
avec has commented on the guide drafted by FEFAC, FEDIOL, COCERAL and COPA-COGECA that Salmonella criteria must apply for all species and that targets, sampling schemes and critical feed material should be covered as well as on farm mixing. Transport is critical and dedicated feed transports may be appropriate.
Adventitious Presence of GM Material in Feed
After more than two years of discussion, the Member States have accepted the proposal of the Commission (SANCO 13368/2010) to harmonise the validation detection methods which include accepting an adventitious presence of non-authorised GM material up to 0.1 per cent in feed ingredients end of June 2011. The proposal is limited to GM feed material authorised for commercialisation in a third country and for which EFSA authorisation is pending for more than three months in the EU.
avec welcomes the proposal together with other stakeholders although the next questions following the proposal is to the threshold levels for food.
December 2011