Perspectives on Poultry World Markets 2011-2012
An overview of the prospects for the global meat industry in general, with a focus on the EU poultry industry from avec, the Association of Poultry Processors and Poultry Trade in the EU Countries, in its annual report for 2011.
Global Agricultural Projections for 2010-2020
According to the projections of OECD-FAO, agricultural production is expected to increase in the short term, assuming normal weather, as a result of an expected supply response to current high prices. Commodity prices should fall from the highs of early 2011, but in real terms are projected to average up to 20 per cent higher for cereals (maize) and up to 30 per cent for meats (poultry), over the 2011-2020 period compared to the last decade.
Global Meat Consumption
Presently, around 16 per cent of global meat consumption takes place in the EU-27. The global demand for proteins from animal products is projected to increase by more than 50 per cent by 2030 compared to that of 2000, due to population growth and increasing wealth especially in developing countries. The trend is expected to continue but will be influenced by environmental, economic and political developments.
Market Situation for Meat
The meat sector is adjusting to the supply and demand imbalances in the feed sector of the past three years. Faced with high production costs, restricted access to credit, high energy costs the supply of poultry meat responded more quickly to the higher demand, and as a result, prices recovered gradually.
Nominal prices for poultry are expected to be 16 per cent higher by 2020 compared to the base period 2008-2010. In real terms, all meat prices are expected to remain firm and on a higher plateau for the 2010-2020 period as to compensate the higher feed and energy costs.
| World meat prices for poultry per period and country | ||||
| Period/Country | Avg 2008-2010 | 2011 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU-27 | US$/t pw(1) | 2.456 | 2.640 | 2.614 |
| Brazil | US$/t rtc(2) | 1.090 | 1.261 | 1.266 |
| USA | US$/t rtc(3) | 1.062 | 1.153 | 1.250 |
Outlook for Global Poultry Meat Production
The livestock sectors are expected to maintain a more even development in the period to 2020. The projections confirm the continuation of the gradual shift in agricultural market's share from developed to developing countries. Latin America, the growth engine of recent years, is expected to be joined by Eastern Europe. Environmental concerns, high input costs, limited additional arable land, ongoing policy reforms and reduced competitiveness because of strong currencies keep agricultural sectors especially in the Western part of Europe roughly at their current levels, barely higher than peak production in 2008.
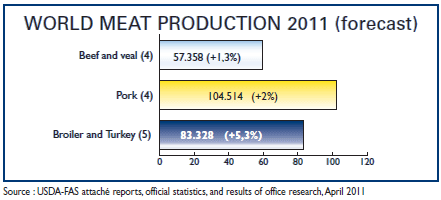
Global poultry meat consumption, on a per-capita basis, is projected to gain importance over the next 10 years, poultry – a relatively inexpensive livestock product is a popular source of protein, especially among poorer populations. Significant per-capita consumption growth is projected for large economies in Asia, the Middle East and some Latin American economies. Poultry meat consumption is expected to expand the fastest (14 per cent), reaching parity with pig meat consumption by the end of the projection period.
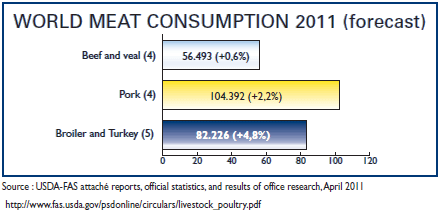
Projection Highlights for Production and Trade of Meat
World meat production growth is anticipated to have an annual reduction of 1.8 per cent, dampened by higher costs during the period 2011-2020, which compares to the 2.1 per cent annually reduction of the previous decade.
The reduced growth is primarily driven by productivity gains from both larger economies of scale and technical efficiency gains, notably for poultry and pig meat in developing countries.
Driven mostly by an expansion of poultry, world meat exports in 2020 are projected to increase annually by 1.7 per cent, in the 2010-2020 period, which compares to 4.4 per cent annually in the previous decade.
A slowing down rate of trade growth in poultry products is anticipated, from an annual rate of 7.7 per cent in last decade to two per cent during the 2010-2020 projection period. US and Brazil, the largest contributors to exported growth, are expected to strengthen their dominance of world trade. During the first period of the projection, their exports will stagnate due to the demand response to high poultry product prices. By 2020, US and Brazilian exports will account for nearly half of the additional export supply in world markets.
Growth in Argentinian exports to the South American market continuously increases. Thailand's exports are also anticipated to expand slightly, mainly for processed products.
Meanwhile the EU exports will decline due to the growing domestic demand, a strong euro and animal welfare regulations limiting stocking density.
Imports growth will be led by countries in Middle East, South Asia and Latin America. Expansion of Mexico's food processing industry is expected to boost the country's import demand due to sustained investment within the processing industry and the continuous need for production material.
Russia, a traditional EU importer, will significantly reduce its imports of poultry following higher domestic production and may become a net exporter of poultry meat. In the EU, the decline in exports during the projection period will be accompanied by a sustained, moderate, expansion of imports. As a result, the EU will see a constant deterioration of its terms of trade, with a balanced account by 2020.
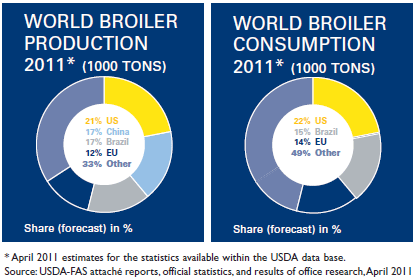
Main Issues and Uncertainties for EU Poultry Meat Trade
- The Russian Federation traditionally an importer of poultry has registered in recent years sustained growth within the Federation to become self-sufficient in poultry meat.
- Will Russia in the future have surplus of production for poultry meat and become a net exporter?
- Will North Africa and Middle East, large importers of EU poultry, have the power to impact world meat trade because of the uncertain political context and civil unrest.
- The World Meat Market is fragmented due to animal health and welfare issues, so the architecture of the 2011-2020 projections can change due to improved conditions by new market players.
- Additional consumer concerns related to animal welfare, food quality, production and processing methods may introduce segmentation in the meat trade chain.
- Any outbreak in a major exporting country, such as Australia, Canada, US and Brazil, which could not be regionalised will affect domestic and international markets.
Further Reading
| - | You can view the previous article from this avec report by clicking here. |
January 2012